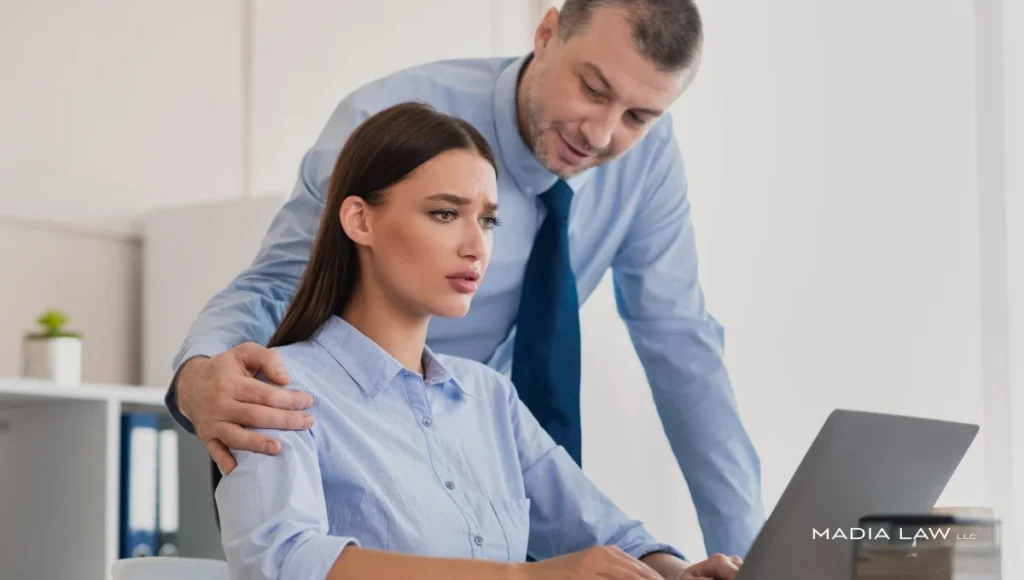
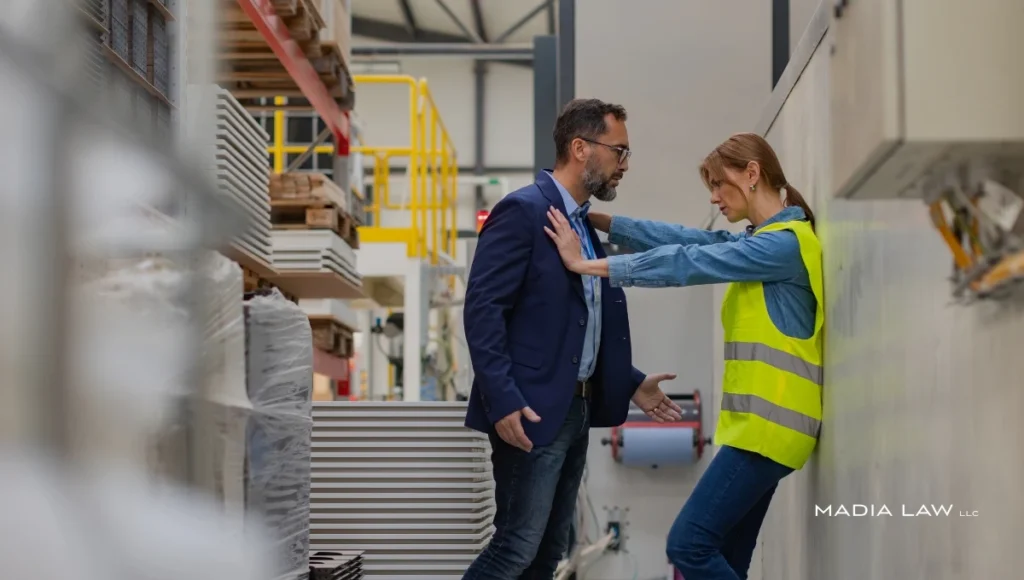
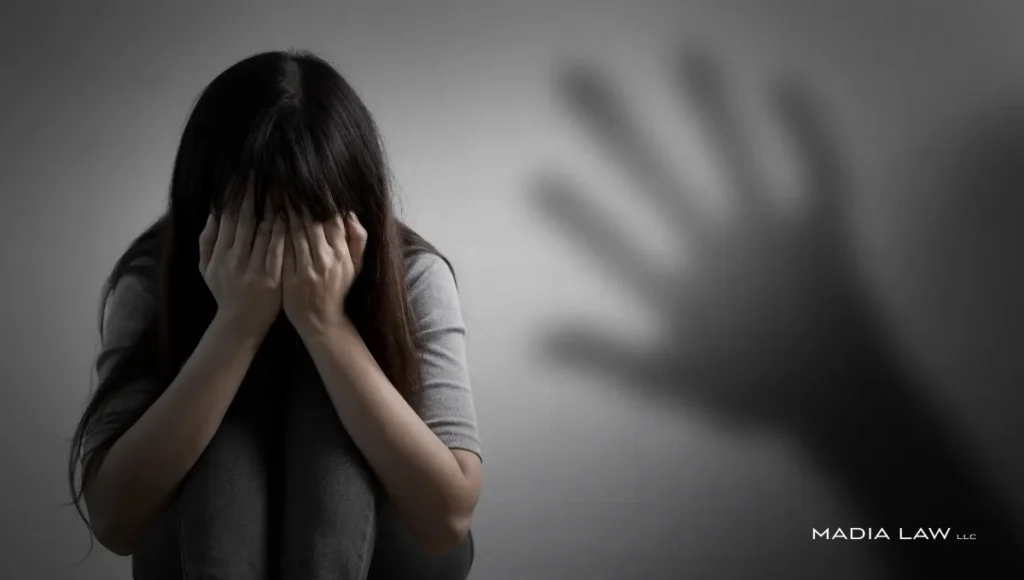
Feeling unsafe at work is never acceptable.
If you’ve found yourself in a professional setting where someone’s words or actions made you feel violated, belittled, or powerless, you’re not overreacting… and there are steps you can take to defend yourself.
You might think to yourself, Can You Sue for Sexual Harassment? Is there a valid legal avenue to escape the feeling of being trapped and go back to living a normal life with security and peace of mind?
Yes, you can sue. Sexual harassment is a real and punishable offense. It’s damaging to not only the victim(s) but the entire workplace, and it’s illegal. Whether it’s a pattern of inappropriate comments, unwanted touching, or intimidating advances, you have the right to take legal action.
At Madia Law LLC, we stand resolutely beside victims of workplace harassment. We fight for your right to work in a space that’s safe, respectful, and free of fear.
What is Sexual Harassment in the Workplace?
Sexual harassment in the workplace is any unwelcome sexual behavior or suggestive innuendo that interferes with your ability to do your job or creates a hostile, intimidating, or offensive environment.
Sexual harassment can be physical (unwanted & inappropriate touches), non-physical (through text, images, calls, and social media), or verbal (negative comments & jokes). A person can be sexually harassed by anyone in the workplace including co-workers, employers, supervisors, and clients/ customers.
This includes:
- Sexual comments or jokes
- Inappropriate touching or staring
- Sexual advances or propositions
- Sharing explicit materials or images
- Retaliating when advances are rejected
These actions are not “just part of the culture.” They’re unequivocal violations of your rights under federal and state law.
For a legal consultation, call 612-349-2729
Types of Sexual Harassment
1. Quid Pro Quo Harassment
Quid Pro Quo harassment occurs when someone in authority demands sexual favors in exchange for job benefits such as promotions, raises, or continued employment.
It often involves implied or explicit threats if those favors are denied. This type of harassment is most common during hiring, performance evaluations, and salary negotiations.
Example: A supervisor tells an employee that their job promotion will be delayed unless they agree to go on a date or engage in sexual conduct.
2. Hostile Work Environment
A hostile work environment is created by repeated or severe sexual comments, gestures, or behaviors that disrupt an employee’s ability to work. This type of harassment damages both mental health and job performance.
It often includes harassment based on protected characteristics such as race, gender, disability, age, or religion.
Example: An employee is repeatedly subjected to offensive jokes, sexually suggestive comments, or degrading nicknames that make the workplace unbearable.
3. Retaliation-Based Harassment
Retaliation harassment happens when an employer or coworker punishes or mistreats someone for reporting sexual harassment or refusing sexual advances. This retaliation can include demotion, exclusion from projects, or termination.
Example: After filing a complaint with HR, an employee is suddenly reassigned to a lower-paying role and excluded from team meetings.
4. Third-Party Harassment
Third-party harassment is committed by individuals outside your organization such as vendors, contractors, customers, or clients. The situation can be exacerbated by your employer failing to stop the misconduct after being made aware.
Example: A client consistently makes inappropriate remarks during meetings, and management refuses to intervene or reassign the account despite repeated complaints.
Categories of Sexual Harassment at Workplace
- Verbal Harassment: Includes inappropriate comments, jokes, sexual innuendo, and verbal abuse.
- Physical Harassment: Involves unwanted touching, blocking movement, or other physical intimidation.
- Visual / Digital Harassment: Sending explicit messages, images, or videos via email, texts, or workplace chats.
- Subtle Harassment: Passive-aggressive behavior or favoritism tied to sexual attention that creates discomfort over time.
Click to contact our personal injury lawyers today
When Can You Sue for Sexual Harassment?
You can sue for sexual harassment when you have evidence that your employer failed to provide a safe and respectful work environment.
Federal and state laws require employers and HR departments to take immediate, effective action when harassment is reported. Failing to do so creates legal liability.
You become eligible to file a lawsuit when the following conditions are met:
- The behavior was unwanted and offensive.
The conduct made you uncomfortable, anxious, or unsafe. - The harassment was repeated or severe.
A single serious event or a pattern of smaller incidents disrupted your ability to work. - You reported it to HR or management.
You took proper internal steps to notify your employer. - HR or management failed to act.
Your complaint was ignored, downplayed, or dismissed without resolution. - You faced retaliation after reporting.
You were demoted, isolated, fired, or punished for speaking up.
Even a single incident may justify legal action if it involves physical assault or a clear abuse of power. The law protects your right to a workplace free of intimidation and abuse, regardless of your job title or length of employment.
Complete a Case Evaluation form now
What to Do if You Are Sexually Harassed at Work
You have the right to speak up. Sexual harassment is not acceptable. One report can protect you and others from future abuse. Taking action is not only brave but also legally protected.
Follow these steps to protect yourself and begin building your legal case:
Step 1: Document Everything
- Write down the dates, times, locations, and exact details of what happened.
- Include what was said or done, and name any witnesses who were present.
- Keep all emails, texts, chat messages, photos, or other evidence in a secure location.
- Use chronological order to track the pattern of misconduct.
Step 2: Confront the Harasser (If Safe to Do So)
- If you feel physically and emotionally safe, tell the harasser directly that their behavior is unwanted, inappropriate, and must stop.
- Use clear and direct language.
- If confronting them could cause further harm, skip this step and proceed to report the harassment formally.
Step 3: Report the Harassment to HR or Management
File a formal report with HR, your supervisor, or another internal authority. Submit it in written form and include:
- The harasser’s name and job title
- A detailed timeline of incidents
- Screenshots or copies of evidence
- Names of witnesses (if any)
After submitting your complaint, monitor how management responds. Keep records of any follow-up communication.
Step 4: Follow Company Policies and Procedures
- Review your employee handbook and follow all outlined steps for internal complaints.
- Take part in any investigation process, including interviews or evidence reviews.
- Monitor your situation for a prompt and fair resolution. The employer must respond appropriately and take corrective action in a timely fashion.
Step 5: Take Care of Your Mental and Emotional Health
Experiencing harassment can take a serious toll on your mental health. Consider speaking with a licensed therapist, joining a support group, or taking medical leave if necessary. Your healing matters as much as your legal action.
What are Your Legal Options if HR Ignores Sexual Harassment Claims?
If your employer or HR fails to address your complaint, you have several legal options to hold them accountable. Inaction is a violation of your rights under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act and state-level protections.
You can take the following legal steps:
- File a Charge with the EEOC
Submit a formal complaint with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). This is the mandatory first step before you can take legal action in court. - Contact an Employment Attorney
An experienced attorney will:- Review your documentation.
- Advise you on your strongest legal path.
- Represent you during communication with the EEOC and in court.
- Request a Right to Sue Letter
If the EEOC investigation does not resolve your case, request a Notice of Right to Sue. You must file your lawsuit within 90 days of receiving this letter. - File a Civil Lawsuit Against Your Employer
You can sue your employer for:- Failing to investigate your complaint.
- Allowing a hostile work environment to continue.
- Retaliating against you after reporting.
- Seek Compensatory and Punitive Damages
You may recover:- Compensation for emotional distress.
- Back pay and lost benefits.
- Punitive damages if the employer acted with willful misconduct or gross negligence.
What Happens After You File a Sexual Harassment Lawsuit?
Filing a lawsuit begins a formal legal process. Here’s what typically happens next:
EEOC Investigation & Mediation Process
After filing, the EEOC opens an investigation within 10 days. They may offer mediation to resolve the case quickly, without going to court.
Employer’s Response & Internal Investigation
Your employer or the accused party receives a notice. They may begin an internal investigation and respond to the EEOC. You may be asked to submit evidence and attend interviews.
Settlement vs. Trial: What to Expect
Most harassment cases settle out of court. If the settlement fails or is not resolved in a satisfactory manner, your attorney will prepare for trial. Outcomes may include financial compensation, policy reform, and disciplinary action against the harasser.
How Long Does a Sexual Harassment Lawsuit Take?
Most cases take 12 to 24 months from filing to resolution. Factors include:
- The complexity of your case.
- Availability of evidence and witnesses
- Court schedules and employer cooperation
Why Hiring a Lawyer for a Sexual Harassment Case is Important
A lawyer protects your rights from the moment you speak up.
They understand employment law, recognize employer defense strategies, and fight to secure justice and full financial recovery.
An experienced sexual harassment attorney can:
- Help you file the EEOC claim correctly: They manage the entire process and file within the 180–300 day deadline, depending on your state.
- Collect evidence and witness testimony: They document key facts, preserve records, and identify credible witnesses to support your claim.
- Represent you in court or during mediation: Whether your case settles or goes to trial, your lawyer presents your case and protects your interests.
- Maximize your financial recovery: They pursue lost wages, emotional damages, and, when justified, punitive damages for employer misconduct.
At Madia Law LLC, we don’t just handle cases – we handle them with care, precision, and compassion.
Stand Up. Speak Out. Get Legal Help Now!
No one should suffer in silence. If you’ve been harassed, ignored, or punished for speaking up for yourself – you have the legal right to sue. At Madia Law LLC, we treat every sexual harassment case with urgency, focus, and compassion. Our trial employment lawyers will:
- Protect your rights.
- Explain your legal options.
- Fight for the justice and compensation you deserve.
Ready for justice? Contact us now, share your case details, and then get in touch with our lawyers. Your voice matters. Your case matters. You matter.
Call 612-349-2729 or complete a Case Evaluation form